What is DVD?
DVD is an optical disc storage format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. It is mainly used for video and audio storage. DVDs can be single- or double-sided, and can have two layers on each side; a double-sided, two-layered DVD will hold up to 17 gigabytes of video, audio, or other information. This compares to 650 megabytes (.65 gigabyte) of storage for a CD-ROM disk. DVDs are of the same dimensions as compact discs (CDs), but are capable of storing more than six times as much data.
DVD Formats
DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVD discs, and is currently the dominant consumer video format in Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and an H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2 decoder (e.g., a DVD player, or a computer DVD drive with a software DVD player). Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination of H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2 compressed video and audio of varying formats (often multi-channel formats as described below). Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 Mbit/s to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate are usually adaptive.
DVD-ROM is the type of drive and disc for use on computers. The DVD drive will usually also play regular CD-ROM discs and DVD-Video disks.
DVD-RAM (DVD–Random Access Memory) is a disc specification presented in 1996 by the DVD Forum, which specifies rewritable DVD-RAM media and the appropriate DVD writers. DVD-RAM media have been used in computers as well as camcorders and personal video recorders since 1998.
DVD-R is a DVD recordable format. A DVD-R typically has a storage capacity of 4.7 GB. Pioneer has also developed an 8.5 GB dual layer version, DVD-R DL, which appeared on the market in 2005.
DVD-Audio (commonly abbreviated as DVD-A) is a digital format for delivering high-fidelity audio content on a DVD. DVD-Audio is not intended to be a video delivery format and is not the same as video DVDs containing concert films or music videos.
There are a number of recordable DVD formats, including DVD-R for General, DVD-R for Authoring, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and DVD+R.
DVD-R and DVD-RW: DVD-R was the first DVD recording format released that was compatible with standalone DVD Players. DVD-R is a non-rewriteable format and it is compatible with about 93% of all DVD Players and most DVD-ROMs. DVD-RW is a rewriteable format and it is compatible with about 80% of all DVD Players and most DVD-ROMs. DVD-R and DVD-RW supports single side 4.37 computer GB* DVDs (called DVD-5) and double sided 8.75 computer GB DVDs(called DVD-10 or DVD-9).
DVD+R and DVD+RW: DVD+R is a non-rewritable format and it is compatible with about 89% of all DVD Players and most DVD-ROMs. DVD+RW is a rewritable format and is compatible with about 79% of all DVD Players and most DVD-ROMs. DVD+R and DVD+RW supports single side 4.37 computer GB* DVDs (called DVD-5) and double side 8.75 computer GB DVDs(called DVD-10 or DVD-9).
DVD+R DL and DVD-R DL: DVD+R DL/DVD-R DL or called DVD+R9/DVD-R9are a Dual Layer writeable DVD+R/DVD-R. The dual layered discs can hold 7.95 computer GB* (called DVD-9) and dual layered double sides 15.9 computer GB (called dvd-18).
DVD-RAM: DVD-RAM has the best recording features but it is not compatible with most DVD-ROM drives and DVD-Video players. Think more of it as a removable hard disk. DVD-RAM is usually used in some DVD Recorders.
DVD-Video and DVD-Audio discs refer to properly formatted and structured video and audio content, respectively. Other types of DVDs, including those with video content, may be referred to as DVD Data discs.
DVD Capacity
There mainly four different DVD sizes:
DVD-5, holds around 4 700 000 000 bytes and that is 4.37 GiB where 1 kbyte is 1024 bytes* . DVD+R/DVD+RW and DVD-R/DVD-RW support this format. It is also called Single Sided Single Layered. This is the most common DVD Media, often called 4.7 GB Media.
DVD-9, holds around 8 540 000 000 bytes and that is 7.95 GiB. DVD+R supports this format. It is also called Single Sided Dual Layered. This media is called DVD-R9, DVD-R DL, DVD+R9, DVD+R DL or 8.5 GB Media.
DVD-10, holds around 9 400 000 000 bytes and that is 8.75 GiB. DVD+R/DVD+RW and DVD-R/DVD-RW support this format. It is also called Double Sided Single Layered.
DVD-18, holds around 17 080 000 000 bytes and that is 15.9 GiB. DVD+R supports this format. It is also called Double Sided Dual Layered.
DVD Recordable and Rewritable
Pre-recorded DVDs are mass-produced using molding machines that physically stamp data onto the DVD. Such discs are known as DVD-ROM, because data can only be read and not written nor erased. Blank recordable DVD discs (DVD-R and DVD+R) can be recorded once using a DVD recorder and then function as a DVD-ROM. Rewritable DVDs (DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and DVD-RAM) can be recorded and erased multiple times.
DVD recordables are now also used for consumer audio and video recording. Three formats were developed: DVD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW (plus), and DVD-RAM. DVD-R is available in two formats, General (650 nm) and Authoring (635 nm), where Authoring discs may be recorded with CSS encrypted video content but General discs may not.
Although most DVD writers can nowadays write the DVD+R/RW and DVD-R/RW formats (usually denoted by “DVD±RW” and/or the existence of both the DVD Forum logo and the DVD+RW Alliance logo), the “plus” and the “dash” formats use different writing specifications. Most DVD readers and players will play both kinds of discs, although older models can have trouble with the “plus” variants.
Disc security
DVD-Video
The Content Scramble System (CSS) is a Digital Rights Management (DRM) and encryption system employed on almost all commercially produced DVD-video discs. CSS utilizes a proprietary 40-bit stream cipher algorithm. The system was introduced around 1996 and was first compromised in 1999.
The purpose of CSS is twofold:
1. CSS prevents byte-for-byte copies of an MPEG (digital video) stream from being playable since such copies do not include the keys that are hidden on the lead-in area of the restricted DVD.
2. CSS provides a reason for manufacturers to make their devices compliant with an industry-controlled standard, since CSS scrambled discs cannot in principle be played on noncompliant devices; anyone wishing to build compliant devices must obtain a license, which contains the requirement that the rest of the DRM system (region codes, Macrovision, and user operation prohibition) be implemented.
While most CSS-decrypting software is used to play DVD videos, other pieces of software (such as DVD Decrypter, AnyDVD, DVD43, Smartripper, and DVD Shrink) can copy a DVD to a hard drive and remove Macrovision, CSS encryption, region codes and user operation prohibition.
DVD-audio
DVD-Audio discs employ a DRM mechanism, called Content Protection for Prerecorded Media (CPPM), developed by the 4C group (IBM, Intel, Matsushita, and Toshiba).
Although CPPM was supposed to be much harder to crack than a DVD-Video CSS, it too was eventually cracked in 2007 with the release of the dvdcpxm tool. The subsequent release of the libdvdcpxm library (which is based on dvdcpxm) allowed for the development of open source DVD-Audio players and ripping software, such as DVD-Audio Explorer. As a result, making 1:1 copies of DVD-Audio discs is now possible with relative ease, much like DVD-Video discs.
Region Codes
DVD region codes are a digital rights management technique designed to allow film distributors to control aspects of a release, including content, release date, and price, according to the region.
This is achieved by way of region-locked DVD players, which will play back only DVDs encoded to their region (plus those without any region code). The commercial DVD player specification requires that a player designed to be sold in a given place play only discs encoded for that region (plus those without any region code). The American DVD Copy Control Association also requires that DVD player manufacturers incorporate the regional-playback control (RPC) system. However, region-free DVD players, which ignore region coding, are also commercially available, and many DVD players can be modified to be region-free, allowing playback of all discs.
DVDs may use one code, a combination of codes (multi-region), every code (all region) or no codes (region free). There are six different official regions and two informal variations.
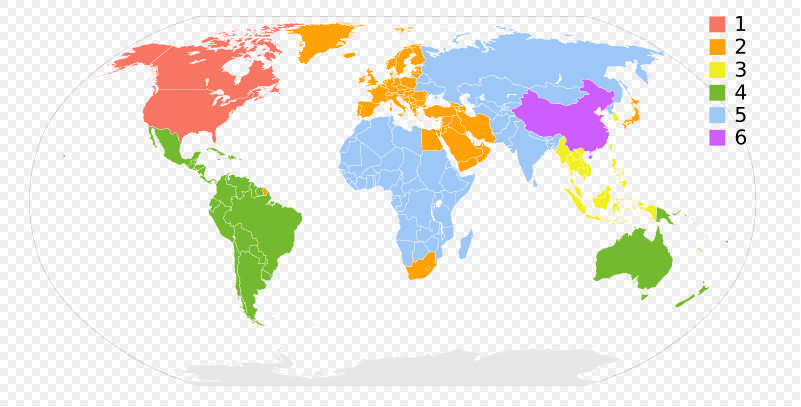
|
Region Codes |
Area |
|
0 |
Informal term meaning “worldwide”. Region 0 is not an official setting; discs that bear the region 0 symbol either have no flag set or have regions 1–6 flags set. Region 0 is commonly referred to as “Region Free”, especially when talking about DVD and Blu-ray Disc players. |
|
1 |
United States, Canada, Bermuda, U.S. territories |
|
2 |
Europe (except Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus), Middle East, Egypt, Japan, South Africa, Swaziland, Lesotho, Greenland, French Overseas departments and territories |
|
3 |
Southeast Asia, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Macau |
|
4 |
South America, Central America, Caribbean, Mexico, New Zealand, Australia, Papua New Guinea and much of Oceania |
|
5 |
Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, Pakistan, Africa (except Egypt, South Africa, Swaziland, and Lesotho), Central and South Asia, Mongolia, North Korea |
|
6 |
China |
|
7 |
Reserved for future use, MPAA-related DVDs and “media copies” of pre-releases in Asia |
|
8 |
International venues such as aircraft, cruise ships, etc. |
|
All |
Region ALL discs have all eight flags set, allowing the disc to be played in any location, on any player. |
You May Also Interest in
No related article